
Reverse Osmosis (RO) is today the most efficient and effective method of water purification technology. It removes dissolved solids, organic matter, biological impurities, metals and chemicals from water.
When water is passed through semi-permeable membrane under pressure, dissolved impurities are captured by membrane effective layer and the water molecules pass through the membrane.
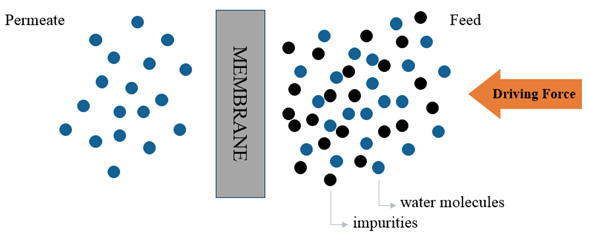
Reverse Osmosis Process
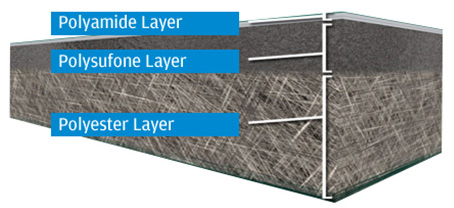
RO membrane is a thin film composite membrane consisting of three layers: a polyester support web, a microporous polysulfone interlayer, and an ultra-thin polyamide barrier layer on the top surface.
RO process applications:
- Drinking water production
- Industrial water production
- Pharmaceutical water production
- Wastewater treatment and reuse
Reverse osmosis processes:
Pretreatment unit:
Pre-treatment refers to the various physical and chemical water treatment processes that perform upstream of the reverse osmosis unit. The objective of pretreatment process is to improve the quality of the raw water to enhance process performance and membranes lifetime.
Depending on the raw water quality, the pretreatment process may consist of the following treatment method:
- Sedimentation
- Floatation
- Media filtration
- Microfiltration/ Ultrafiltration
- Ion exchange
Reverse osmosis unit:
RO section consists of high pressure pump, pressure vessels and RO membranes. Reverse osmosis driving force is provided by high pressure pumps. The HP pump raises process pressure and feeds water into the reverse osmosis membrane elements. Pressurized feed water is separated to desalinated permeate and concentrated brine streams in each RO element.
Post treatment unit:
Depending on the treated water application, the Reverse Osmosis permeate should be conditioned before usage.
Post treatment methods:
- Demineralization
- Re-mineralization
- Disinfection
- pH adjustment
